

At the previous Tokyo Motor Show, Mitsubishi exhigited the ESR (Ecological Science Research) experimental vehicle. This car introduced some revolutionary technologies designed to protect the environment.
Since then, Mitsubishi has further evolved and refined those technologies. The result is the Mitsubishi HEV (Hybrid Electric Vehicle).
HEV achieves the seemingly contradectory goals of eco-friendly driving with the power of a conventional artomobile. Though now an experimental model, HEV was developed with the goal of future practical use.
 Mult-mode system for clean performance
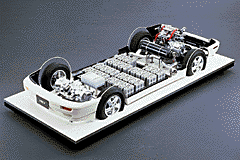
Mult-mode system for clean performanceHEV automatically switches between battery and hybrid driving modes to provide ecologically clean driving with efficient use of energy.
In urban areas, HEV uses only its batteries, for zero emission driving. When the batteries run down, HEV enters hybrid mode, as the low emission engine recharges the batteries. In addition, when the accelerator is reseased or the brake pedal is depressed, the braking energy recovery system kicks in to return electricity from the motors to the batteries.
| Overall length | 4,785mm |
|---|---|
| Overall midth | 1,695mm |
| Overall height | 1,595mm |
| Wheelbase | 3,000mm |
| Track F/R | 1,455/1,460mm |
| Passengers | 4 |
| Battery (V/no.) | 336V / 30 |
| Motor type | A/C inductor (twin) |
| Max.output | 60kW |
| Max.torque | 19.6kgm |
| Engine displacement | 4-cylinder 1.5litre |
| Fuel | Compressed Natural Gas |
| Emissions control devices | Electric/ternary catalyst |
| Output | 20kW |
| Transmission | 2-speed semi auto |
| Steering | Electro-hydraulic power assisted |
| Suspension (F/R) | Macpherson strut / semi-trailing |
| Brakes (F/R) | DISC/DRUM |
| Tire | 205/70R14 low-resistance |

NEXT TOPIC:"MBECS-III"

![]() Copyright 1995 by Mitsubishi Motors Corporation.
Copyright 1995 by Mitsubishi Motors Corporation.