

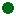
 AYC Profile
AYC Profile
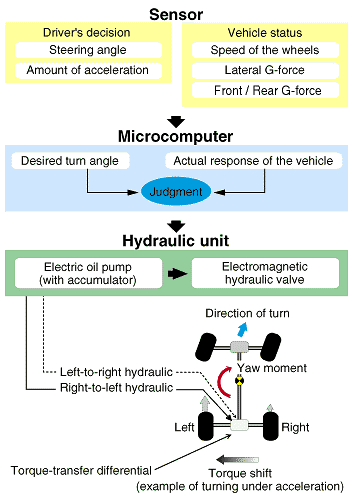
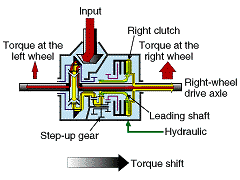
| The Torque Transfer Differential comprises: (1) A Gear Mechanism which generates, inside differential, two differing rotational speeds which are 'fast" or "slow" relative to the rotational speed of the differential case and; (2) A Left/Right Clutch Which employs the differential in the rotational speeds in (1) to transfer is able to transfer drive torque between the left and right wheels at will and with practically no energy losses; something not possible in conventional limited slip differentials (LSD). | |
 | 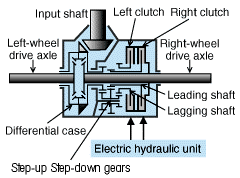 |
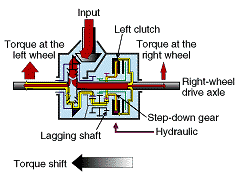
1.Shifting torque to the rightWhen the right clutch is engaged while letting it slip, torque in proportion t o the degree of engagement is shifted from the "leading shaft, " which has the faster rotation, to the right-wheel drive axle, which has the slower rotation, thereby increasing torque to the right wheel and decreasing torque to the lef t wheel. |
2.Shifting torque to the leftWhen the left clutch is engaged, the torque is shifted from the right-wheel dr ive axle, which has the faster rotation, to the "lagging shaft," which has the lower rotation, resulting in decreasing the torque to the right wheel and inc reasing torque to the left wheel. |
|
|
